I was working in an environment that had virtual desktops (managed by horizon view) that were secured using agent less antivirus using Trend Micro Deep Security in integration with vShield manger. As vShield manager is not supported platform anymore - the plan was to migrate from vShield manager to NSX Manager and integrate it with Trend Micro Deep Security. Here are the steps that we followed in the whole process -
- Deploy NSX Manager from vCenter.
- Logon to NSX manager and configure the NTP settings for the NSX manager.
- Configure the inventory services and register vCenter to the NSX manager. SSO admin credentials (e.g.- administrator@vSphere.local) are required for this configuration.
- Once the inventory service and vCenter are connected successfully with NSX Manager, logon to vCenter with SSO admin credentials (the same credentials that were used to register the vCenter with NSX Manager) - Networking and Security (NSX manager) icon will pop up in vCenter.
- Add the required users to the NSX manager - so they can manage the NSX manager using their own credentials.
- Add the NSX license to the vCenter and assign the license to the NSX manager solution.
- At this point you can start the migration of vShield to NSX manager.
- Take the necessary backups before proceeding the migrations.
- Disable the desktop provisioning for the vCenter using view admin console.
- NSX Manager works on ESXi cluster basis. If you are planning to apply the NSX manager integration with deep security on particular ESXi cluster - all hosts under that cluster needs to be cleaned up with filter driver, DVSA appliance and vShield endpoint.
- Logon to Trend Micro Deep Security manager (admin console) and uninstall the filter driver for all required hosts. From trend micro manager, go to Computers - navigate to the host for which you want to remove the filter driver, click on actions - remove filter driver. The hosts will be placed in maintenance mode and will be rebooted.
- Once the reboot is complete, take the host out of maintenance mode and delete the trend micro (DVSA) appliance.
- Once the DVSA appliance is deleted, logon to the vShield manager admin console, and uninstall the vShield end point for those hosts. Logon to vShield manager - select the host (for which filter driver and DVSA appliance is already removed) - from right side pane - click on vShield endpoint - uninstall. The new wizard will pop up. Select the vShield endpoint and then click uninstall. The host needs to be out of maintenance mode for removing end point.
- Once the end point is removed from the host - restart the host.
- Once all hosts in the cluster are cleaned up - you are ready to deploy NSX manager vibs and appliances on these hosts. Remember - if you are placing any VMs to these hosts at this point they won't be having any security.
- Remove the vShield manager plugin from the Trend micro manager. Make sure that you are not performing this step before removing the filter driver, else you will lose the ability to uninstall the filter driver from ESXi host using Trend Micro Deep Security Manger console - as the "action" tab for host will disappear once the vShield manager is removed from the Deep security console.
- If happen so, you can either add back the vShield manager to Trend micro manager or you can uninstall the filter driver vibs manually from the host using following commands.
# esxcli software vib list
#esxcli software vib uninstall VIBNAME
- Shutdown the vShield manager appliance. This step is IMPORTANT as trend micro may freak out as it sometime starts checking for vShield manager though NSX manager is connected to Trend Micro Deep Security.
- Once the vShield manager is removed, add the NSX manager in place of it. Add the certificate, accept the certificate, test the connection and make sure everything is green.
- Right click on the vCenter again and synchronize the properties.
- Go back to NSX manager and check if the trend micro services are showing up. Go to NSX Manager - Service Definition and on the right side pane check the services - Trend micro deep security security service should be popped up. If so, the integration is successful between NSX manager and Trend Micro Deep Security.
- Now perform the host preparation for the cluster that are cleaned up initially from vShield. Select the cluster and click on actions - Install.
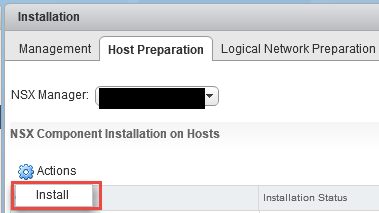
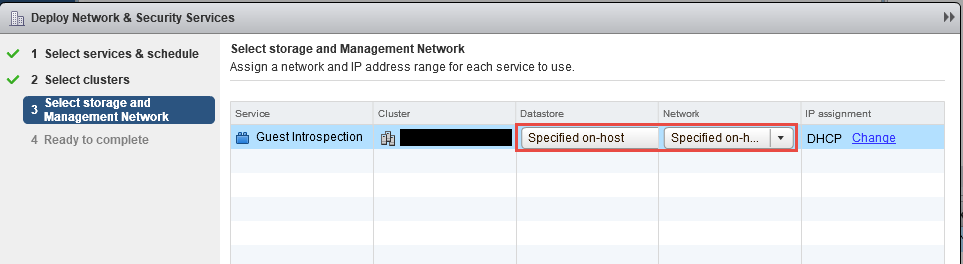
- Once the host preparation is complete proceed with deploying the appliances. Click on Installation under NSX manager - from right side pane click on service deployment. Select the "+" sign and follow the wizard to complete the deployment. The appliances needs to be deployed in sequence - that is guest introspection and then trend micro deep security appliance.
- While placing the appliance, they can be placed on specific data store and network. The setting can also be defined on ESXi host directly under agent VM section, and then select the appliance specification as specified on host" while deploying the appliance.

- The deployment of appliances does take long time (may be more than hour), especially if the cluster have more number of hosts (8 and above).
- Once all these appliances are deployed - create the security group and security policy from NSX manager. Then apply the policy to security group.
- If everything is configured correctly, you will see the trend micro manager activating the VMs.
- Check if there are any VMs that are being managed by the new trend micro deep security appliance. It may take a while to see the VMs under security appliance. Test the VM for security by downloading test virus. It should get deleted swiftly.






Comments
Post a Comment